How to Calculate Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
Mean arterial pressure (MAP) is the average pressure in a patient's arteries during one cardiac cycle. It's a crucial vital sign used to assess the adequacy of blood perfusion to vital organs. Understanding how to calculate MAP is essential for healthcare professionals and anyone interested in health monitoring. This guide will walk you through the process, explaining the formula and its significance.
Understanding the Components: Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure
Before diving into the calculation, let's clarify the two key components:
-
Systolic Blood Pressure: This is the higher number in a blood pressure reading, representing the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats and pumps out blood.
-
Diastolic Blood Pressure: This is the lower number, indicating the pressure in your arteries when your heart rests between beats.
Both systolic and diastolic pressures are measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
The MAP Formula
The most common formula used to calculate mean arterial pressure is:
MAP = (Systolic Blood Pressure + 2 * Diastolic Blood Pressure) / 3
Let's break down why we use this formula: Diastolic pressure lasts approximately twice as long as systolic pressure during a cardiac cycle. Multiplying the diastolic pressure by 2 accounts for this duration difference.
Example Calculation
Let's say a patient's blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg (systolic/diastolic). Here's how we calculate their MAP:
MAP = (120 + 2 * 80) / 3 MAP = (120 + 160) / 3 MAP = 280 / 3 MAP = 93.3 mmHg (approximately)
Therefore, the patient's mean arterial pressure is approximately 93.3 mmHg.
Why is MAP Important?
MAP is a vital indicator of tissue perfusion – the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the body's tissues. A low MAP can suggest insufficient blood flow, potentially leading to organ damage. Conversely, a consistently high MAP can indicate hypertension and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
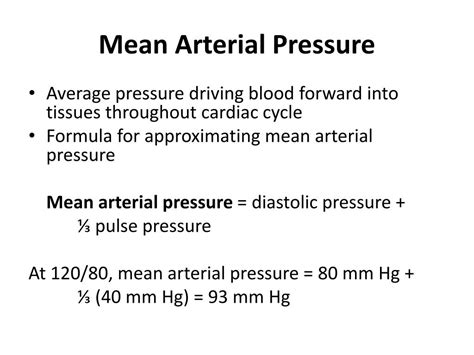
Alternative MAP Calculation (Simplified)
While the standard formula is most accurate, a simplified estimation can be used in certain clinical situations where quick assessment is needed:
MAP ≈ Diastolic Blood Pressure + (Pulse Pressure / 3)
Where pulse pressure is the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure (Systolic BP - Diastolic BP). This method offers a quicker calculation but is less precise than the primary formula.
Factors Affecting MAP
Several factors influence MAP, including:
- Cardiac Output: The amount of blood pumped by the heart per minute.
- Systemic Vascular Resistance: The resistance to blood flow in the arteries.
- Blood Volume: The total amount of blood in the circulatory system.
Conclusion
Calculating mean arterial pressure is a straightforward yet critical process in assessing cardiovascular health. By understanding the formula and the significance of MAP, healthcare professionals and individuals can better monitor their health and identify potential problems early on. Remember to always consult with a healthcare provider for any concerns about your blood pressure or cardiovascular health.