How to Reverse Fatty Liver Disease: A Comprehensive Guide
Fatty liver disease, or hepatic steatosis, is a condition where excessive fat accumulates in the liver. While it often presents with no symptoms, it can lead to serious health problems like cirrhosis, liver failure, and even liver cancer if left untreated. Fortunately, in many cases, fatty liver is reversible with lifestyle changes. This comprehensive guide will explore effective strategies for managing and potentially curing fatty liver disease.
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
Before diving into treatment, it's crucial to understand the different types of fatty liver disease:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): This is the most common type, linked to factors like obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, and metabolic syndrome. It's not caused by excessive alcohol consumption.
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD): This type, as the name suggests, is directly related to excessive alcohol intake.
This guide focuses primarily on NAFLD, as it's the more prevalent form. However, many strategies apply to both types. It's essential to consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. They can perform tests to determine the severity of your condition and rule out other liver diseases.
Lifestyle Changes: The Cornerstone of Fatty Liver Treatment
Lifestyle modifications are the cornerstone of treating NAFLD. These changes often lead to significant improvement and, in some cases, complete reversal of the condition. Here's a breakdown of key strategies:
1. Weight Management: The Most Critical Factor
Losing even a modest amount of weight (5-10%) can dramatically improve liver health. This is arguably the most effective strategy. Focus on sustainable weight loss through a combination of diet and exercise. Avoid crash diets, as these can be detrimental to your overall health.
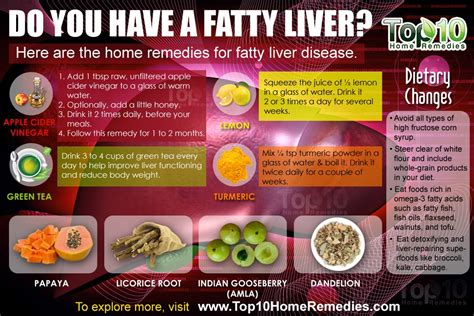
2. Dietary Changes: Fueling Your Liver's Recovery
- Reduce refined carbohydrates: Limit sugary drinks, white bread, pastries, and processed foods. These contribute to excess fat accumulation in the liver.
- Increase fiber intake: Fiber helps regulate blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet.
- Choose healthy fats: Incorporate sources of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats like olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds.
- Limit saturated and trans fats: These are found in red meat, processed foods, and fried foods. They should be minimized in your diet.
- Increase protein intake: Protein supports liver repair and helps maintain muscle mass during weight loss. Choose lean protein sources like chicken, fish, beans, and lentils.
3. Regular Exercise: Boosting Metabolism and Liver Function
Regular physical activity is essential for weight management and overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling. Incorporate strength training exercises at least twice a week to build muscle mass.
4. Managing Underlying Conditions: Addressing the Root Cause
If you have diabetes, high cholesterol, or metabolic syndrome, effectively managing these conditions is crucial for improving liver health. Work closely with your doctor to develop a treatment plan for these underlying issues.
Medical Interventions: When Lifestyle Changes Aren't Enough
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be sufficient to reverse fatty liver disease. Your doctor might recommend additional interventions, such as:
- Medication: Certain medications can help manage related conditions like diabetes and high cholesterol, indirectly improving liver health.
- Further Investigations: If the condition progresses, more in-depth testing may be needed to assess liver function and rule out other complications.
Monitoring and Follow-up: The Long-Term Perspective
Regular follow-up appointments with your doctor are crucial to monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as needed. Blood tests and imaging studies can help track your liver health and ensure the effectiveness of your treatment strategies.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of fatty liver disease or any other medical condition. The information provided here is not a substitute for professional medical advice.