How to Lower Blood Glucose Levels Naturally and Effectively
High blood glucose levels, or hyperglycemia, can be a serious concern, leading to various health complications if left unmanaged. This comprehensive guide explores natural and effective ways to lower your blood glucose levels, empowering you to take control of your health. We'll cover dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and the importance of regular monitoring. Remember, this information is for educational purposes and should not replace advice from your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your diet or lifestyle, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions.
Dietary Strategies for Lowering Blood Glucose
Dietary changes are often the cornerstone of managing blood glucose levels. Focusing on the right foods can significantly impact your overall health and well-being.
1. Prioritize Low-Glycemic Index Foods:
The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar. Opting for low-GI foods helps prevent sharp spikes in blood glucose. These include:
- Non-starchy vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, peppers.
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans.
- Whole grains: Oats, quinoa, brown rice (in moderation).
- Fruits (in moderation): Berries, apples, pears.
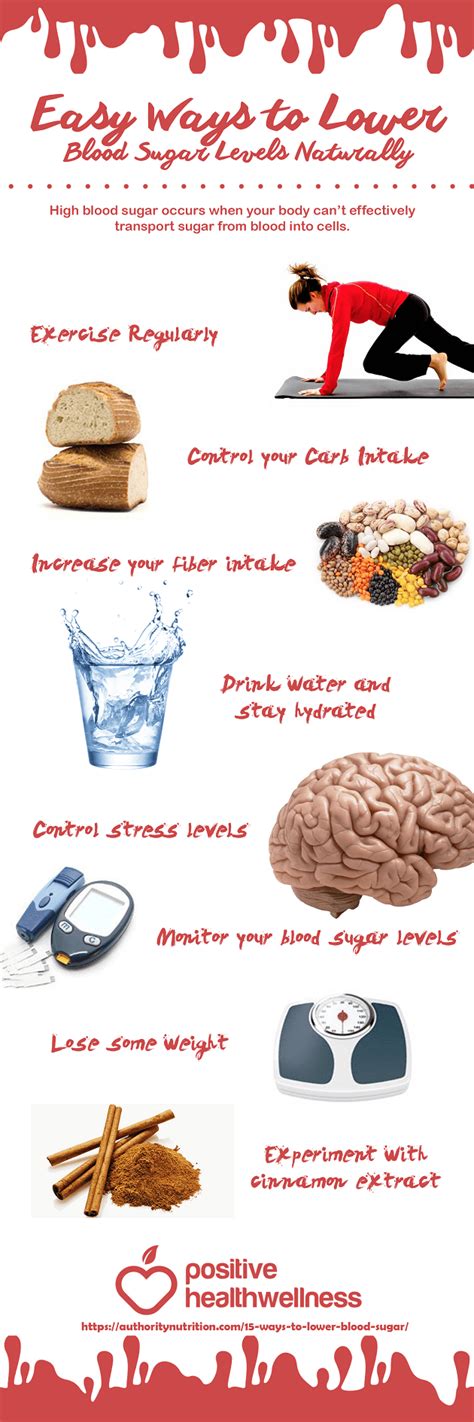
2. Control Carbohydrate Intake:
While carbohydrates are essential, controlling their portion sizes is crucial. Avoid refined carbohydrates like white bread, pasta, and sugary drinks, as these are quickly digested and lead to rapid blood glucose increases.
3. Increase Fiber Intake:
Fiber slows down glucose absorption, preventing spikes in blood sugar. Good sources include:
- Fruits and vegetables: As mentioned above, they're packed with fiber.
- Whole grains: Choose whole-wheat bread, brown rice, and oats over refined grains.
- Legumes: Excellent sources of both fiber and protein.
4. Choose Lean Protein Sources:
Protein helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes satiety, preventing overeating. Include:
- Fish: Salmon, tuna, cod.
- Poultry: Chicken, turkey.
- Beans and lentils: Excellent plant-based protein sources.
- Nuts and seeds: Healthy fats and protein combined.
5. Healthy Fats are Your Friend:
Unsaturated fats, found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, can help improve insulin sensitivity. Limit saturated and trans fats found in processed foods.
Lifestyle Modifications for Blood Glucose Control
Beyond diet, lifestyle plays a crucial role in managing blood glucose levels.
1. Regular Exercise:
Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, helping your body utilize glucose more effectively. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
2. Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for blood glucose control. Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly impact your blood sugar levels.
3. Stress Management:
Stress can elevate blood glucose levels. Practice stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
4. Adequate Sleep:
Getting enough sleep (7-9 hours per night) is vital for overall health and can positively influence blood glucose regulation.
Monitoring Your Blood Glucose Levels
Regularly monitoring your blood glucose levels is essential to understand how your diet and lifestyle choices affect your blood sugar. This allows for adjustments to optimize your management plan. Consult your doctor or healthcare provider to determine the best monitoring method for you.
Conclusion
Lowering blood glucose levels is achievable through a combination of dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring. By incorporating the strategies outlined above, you can take proactive steps to improve your health and well-being. Remember to always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance. This information is intended for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice.