How to Take Blood Pressure Manually: A Step-by-Step Guide
Taking your blood pressure manually using a sphygmomanometer and stethoscope might seem daunting, but with practice, it becomes a straightforward process. This guide provides a comprehensive, step-by-step approach, ensuring accurate readings and contributing to better health management. Understanding how to do this empowers you to monitor your health effectively.
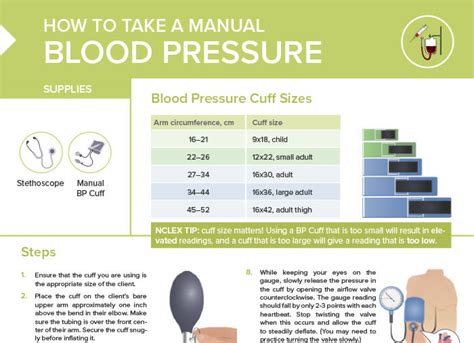
Essential Equipment
Before you begin, ensure you have the necessary tools:
- Sphygmomanometer: This is the inflatable cuff and pressure gauge. There are two main types: aneroid (uses a needle on a dial) and mercury (uses a column of mercury, less common now due to safety concerns). Both work similarly.
- Stethoscope: This is crucial for listening to your heartbeats. Choose a stethoscope with good acoustic quality for accurate sound detection.
Preparing for the Measurement
Finding the Right Position:
- Sit comfortably: Find a chair with back support, ensuring your feet are flat on the floor. Avoid crossing your legs.
- Rest for 5 minutes: Allow yourself time to relax before taking the reading. Stress and physical activity can influence blood pressure.
- Bare arm: Expose your upper arm. The cuff needs to fit snugly against your skin. Avoid tight clothing that might interfere with the reading.
Positioning the Cuff:
- Locate brachial artery: The brachial artery is located on the inside of your upper arm, slightly above the elbow crease.
- Proper cuff placement: The lower edge of the cuff should be about an inch above your elbow crease. The artery should be centered under the cuff. The cuff needs to be snug, but not too tight.
The Measurement Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
-
Inflate the cuff: Slowly pump up the cuff using the bulb until the pressure gauge reaches around 30 mmHg above your anticipated systolic pressure (explained below). If you're unsure, start at around 160 mmHg.
-
Listen with the stethoscope: Place the diaphragm (the flat side) of your stethoscope firmly over the brachial artery, ensuring a good seal.
-
Deflate the cuff slowly: Slowly release the valve on the cuff, allowing the pressure to drop gradually at a rate of approximately 2-3 mmHg per second.
-
Identify systolic and diastolic pressure:
- Systolic pressure: This is the first clear tapping sound you hear as the pressure in the cuff decreases. This is the higher number in your blood pressure reading. Record this number.
- Diastolic pressure: This is the point where the sounds disappear completely. This is the lower number in your blood pressure reading. Record this number.
-
Record your reading: Note both the systolic and diastolic readings (e.g., 120/80 mmHg). It's important to record the reading accurately and to take multiple readings to get a more accurate average.
Interpreting Your Blood Pressure Reading
Your blood pressure reading will be represented as two numbers: systolic/diastolic. For example, 120/80 mmHg. High blood pressure (hypertension) is generally considered to be 140/90 mmHg or higher. However, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional to interpret your readings and discuss any concerns. Regular monitoring and adherence to a healthy lifestyle are vital for maintaining optimal blood pressure.
Tips for Accuracy
- Practice makes perfect: The more you practice, the more confident and accurate you'll become.
- Multiple readings: Take at least two readings, separated by a minute or two, to ensure accuracy.
- Proper cuff size: Using a cuff that's too small or too large will result in inaccurate readings. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for advice on proper cuff size.
- Avoid distractions: Minimize distractions during the measurement process.
- Regular maintenance: Ensure your stethoscope and sphygmomanometer are well-maintained.
By following this comprehensive guide, you'll gain the knowledge and skills to accurately take your blood pressure manually, contributing to your overall health awareness and proactive healthcare management. Remember, this guide is for informational purposes, and it's always essential to consult your physician for any health concerns.