How to Advocate as a Nurse for an LVAD Procedure
Nurses play a crucial role in advocating for their patients, particularly when complex procedures like Left Ventricular Assist Device (LVAD) implantation are considered. This process requires navigating complex medical information, patient wishes, and healthcare systems. This guide will help nurses effectively advocate for their patients needing an LVAD.
Understanding the LVAD Procedure and Patient Needs
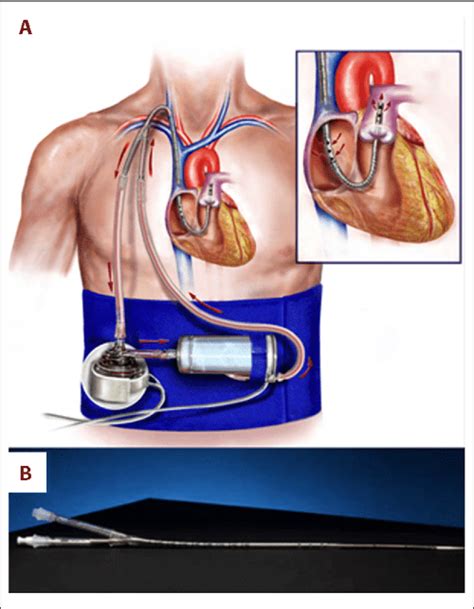
Before advocating for an LVAD, a thorough understanding of the procedure and the patient's specific needs is paramount. An LVAD is a mechanical pump that assists the heart in pumping blood. It's a life-sustaining treatment for patients with severe heart failure who are not candidates for heart transplant.
Key considerations before advocating:
- Patient's medical history: A comprehensive understanding of the patient's cardiac history, including ejection fraction, symptoms, and response to previous treatments, is crucial.
- Severity of heart failure: Assessing the patient's functional capacity, quality of life, and the urgency of their condition is vital. Are they experiencing frequent hospitalizations? Is their quality of life significantly impaired?
- Patient's wishes and understanding: Open communication with the patient and their family regarding the risks, benefits, and alternatives to LVAD implantation is essential. Ensuring informed consent is paramount.
- Resource availability: Consider the availability of post-operative care, including access to specialized LVAD clinics and support systems.
Steps to Effectively Advocate for an LVAD
Advocating for an LVAD involves a multi-step process requiring careful planning and communication.
1. Gathering Comprehensive Patient Data
Thoroughly document the patient's clinical presentation, including:
- Detailed medical history: This should include previous treatments, response to medications, and any complications.
- Current symptoms: Clearly document the patient's symptoms, their severity, and their impact on their daily life. Use quantifiable measures whenever possible (e.g., "patient reports shortness of breath with minimal exertion").
- Laboratory results: Include all relevant blood tests, including cardiac biomarkers and electrolytes.
- Imaging studies: Gather reports from echocardiograms, cardiac catheterizations, and any other relevant imaging.
2. Building a Strong Case for LVAD
Based on the collected data, build a compelling case that justifies the need for an LVAD. This involves:
- Highlighting the severity of heart failure: Emphasize the patient's declining functional status and the limitations imposed by their condition.
- Demonstrating the failure of alternative treatments: Explain why other treatment options have been unsuccessful or are no longer appropriate.
- Presenting the benefits of LVAD: Clearly articulate how an LVAD can improve the patient's quality of life, extend their lifespan, and reduce the frequency of hospitalizations.
- Addressing potential risks and complications: Honestly discuss the risks associated with LVAD implantation, including infection, bleeding, and device malfunction.
3. Effective Communication with the Healthcare Team
Clear and concise communication is critical in advocating for your patient.
- Collaborate with the cardiologist: Work closely with the cardiologist to ensure they have all the necessary information to make an informed decision.
- Present a well-organized case: Use the gathered data to create a concise and persuasive presentation that clearly articulates the patient's needs and the rationale for LVAD implantation.
- Engage in respectful discussions: Maintain a professional and respectful manner during discussions with the healthcare team, even when facing disagreements.
- Document all communications: Maintain detailed records of all conversations, decisions, and any challenges encountered throughout the process.
4. Supporting the Patient and Family
Providing emotional support to the patient and their family is crucial.
- Educate the patient and family: Explain the LVAD procedure, its benefits and risks, and the post-operative care requirements in a clear and understandable manner.
- Address their concerns: Listen actively to their concerns, answer their questions honestly, and provide emotional support throughout the process.
- Empower the patient: Involve the patient in decision-making, respecting their autonomy and preferences.
By following these steps, nurses can effectively advocate for their patients needing an LVAD procedure, improving patient outcomes and ensuring access to potentially life-saving treatment. Remember, patient advocacy is a vital aspect of nursing care, requiring strong communication, clinical knowledge, and unwavering commitment to the patient's well-being.