I cannot provide medical advice, and this information is for educational purposes only. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for any concerns about infertility. They can provide accurate diagnoses and treatment options. Self-diagnosing infertility is dangerous and inaccurate.
How to Determine if a Woman Might Be Experiencing Infertility: Understanding the Process
Infertility is a complex issue, and determining if a woman is infertile requires professional medical evaluation. There's no home test to definitively diagnose infertility. However, certain factors and symptoms can indicate the need for a consultation with a fertility specialist or gynecologist. This article outlines some key aspects to consider, but it is vital to remember that this information is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Recognizing Potential Indicators of Infertility
Several factors can contribute to infertility, and identifying potential indicators requires a comprehensive understanding of reproductive health. While these are not definitive diagnoses, they warrant a visit to a healthcare professional:
1. Difficulty Conceiving After a Year of Trying
The most common indicator of potential infertility is the inability to conceive after one year of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse. This timeframe is often used as a benchmark for seeking professional help.
2. Irregular or Absent Menstrual Cycles
A woman's menstrual cycle provides vital information about her reproductive health. Irregular cycles (cycles that vary significantly in length) or the complete absence of menstruation (amenorrhea) can be indicative of underlying hormonal imbalances that may impact fertility.
3. History of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
PID is an infection of the female reproductive organs. If left untreated, PID can lead to scarring and damage to the fallopian tubes, significantly impacting the chances of conception. A history of PID should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
4. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus. This can lead to pain, heavy bleeding, and infertility.
5. Age
A woman's age plays a significant role in fertility. As women age, their egg quality and quantity decline, reducing the chances of conception. This is particularly relevant after age 35.
6. Other Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid problems, and certain autoimmune diseases, can affect fertility.
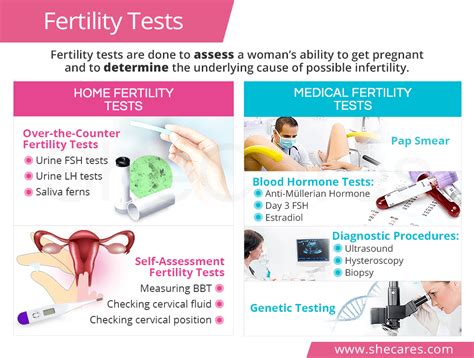
The Importance of Professional Testing and Diagnosis
It is impossible to reliably test for infertility at home. If you suspect you might be experiencing infertility, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional. They will conduct a comprehensive evaluation, which may include:
- Pelvic exam: To assess the reproductive organs.
- Hormone testing: To check hormone levels and identify potential imbalances.
- Ovulation tests: To confirm ovulation is occurring.
- Ultrasound: To visualize the reproductive organs and assess their structure.
- Semen analysis: For the male partner, to assess sperm health and count. Infertility is a partnership issue, and both partners should be evaluated.
- Hysterosalpingogram (HSG): A test to check the patency (openness) of the fallopian tubes.
- Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive surgical procedure that can help diagnose endometriosis and other conditions.
Navigating the Path to Seeking Help
Don't hesitate to seek medical advice if you are concerned about your fertility. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve your chances of conception. Your doctor can guide you through the testing process and provide the best options for your specific situation. Remember, you're not alone. Many couples experience challenges with infertility, and there are resources and support available.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.